Mexico’s Election Impact on Energy Policy
Background
On 2nd June 2024, Claudia Sheinbaum made history by being elected as Mexico’s first female president. With a strong academic background, Sheinbaum is a physicist holding a doctorate in energy engineering and was part of the Nobel Peace Prize winning UN panel on climate change. Sheinbaum’s economic agenda aims to capitalise on the opportunities presented by American nearshoring efforts, contingent on a stable and expanding energy supply.
Mexico is one of the largest oil suppliers in the world, having produced 1.6 million barrels daily in 2022. The country is also ranked 13th in the global crude oil output. Whilst Sheinbaum has promised to accelerate Mexico’s clean energy transition and aims to generate 50% of its energy from renewables by 2030, most spectators are divided. Some hope her scientific background will lead to a greater emphasis on clean energy, while others fear she might follow the policies of her predecessor, Andrés Manuel López Obrador, who invested heavily in bolstering fossil fuel-reliant state energy companies, PEMEX (Petróleos Mexicanos) and CFE (Comisión Federal de Electricidad).
Regardless of her position on energy transition, Sheinbaum faces the challenge of restoring investor confidence, which was shaken during López Obrador’s administration. Without this achievement, the new leader cannot guarantee Mexico’s energy stability and it could jeopardise the country’s commitment under the US - Mexico - Canada Agreement (USMCA) and the Paris Agreement.
Mexico’s gas supply, traditionally dominated by PEMEX, faced disruptions due to declining production and pipeline congestions. An energy reform in 2013 allowed private firms to enter the gas market to boost market competition and supply reliability. However, under López Obrador, the private sector participation was viewed as a threat, and efforts were allocated to prioritise PEMEX’s production. Currently, the company is the most indebted oil corporation in the world, with its stocks having a -5.74% 3-year return, compared to +11.48% from other companies in the same period and sector.
Considerations for Sheinbaum’s Energy Strategy
Sheinbaum has a decision to make regarding the energy future of Mexico. There is a confluence of energy-related factors that Sheinbaum will need to consider early in her administration, such as increasing domestic energy demands, pressure from environmental groups and international climate regimes, a deepened reliance on energy imports from abroad, and foreign companies’ dissatisfaction with the state’s current control of the energy sector.
Sheinbaum has long supported the state-centric energy policies of the previous administration, including legislative amendments that rolled back the 2013 constitutional reforms that helped liberalise the Mexican energy sector. Nevertheless, while Sheinbaum continues to defend the energy policies of the previous López Obrador administration, she is more pragmatic than her predecessor, which may provide a path for potential policy change to deal with the various energy issues facing her administration.
One area where Sheinbaum differs from López Obrador is the role of renewable energy sources in Mexico’s energy mix. Sheinbaum has a robust environmental pedigree and has published extensively on the clean energy transition. During her time as mayor of Mexico City, she implemented clean energy infrastructure and electrified transportation modalities. Furthermore, according to her campaign platform, she is committed to progressing Mexico’s clean energy transition and decarbonising the economy. However, climate progress under the Sheinbaum administration is likely to be tempered by fossil fuel supporters. Mexico still strongly depends on the oil and gas industry for its energy needs, accounting for over 80% of its energy mix in 2022. Understanding the necessity of oil and gas for the domestic economy, Sheinbaum has championed domestic oil production and supports the central role of PEMEX in the energy sector.
Source: IEA (2024)
As Mexican energy sovereignty will likely continue to be a focus for Sheinbaum’s administration, issues related to weak foreign direct investment in the Mexican energy industry are likely to persist. Under the current policy framework, private industry does not have an incentive to invest in exploration and production activities in Mexico. Lax private investment coupled with recent financial struggles at PEMEX may result in insufficient investment in Mexico’s energy infrastructure and increased reliance on energy imports. Therefore, to address the increased domestic energy demands, Sheinbaum may alter the government's prevailing energy strategy to ensure sustainable and robust energy supplies by providing private companies more control/access to the energy sector.
There are also broader trade implications regarding Sheinbaum’s potential approach to Mexico’s energy strategy, particularly how it impacts the country’s relationship with the US. The US Trade Representative communicated to its Mexican counterpart that the legislative amendments passed under the López Obrador administration violated investment provisions stipulated by the USMCA, leading the US to open dispute settlement consultations to address the issue. If a negotiated agreement is not reached, the US could invoke trade sanctions targeting Mexico in response. Failure to reaffirm Mexico’s commitment to the trade agreement could also lead to neglect of economic opportunities stemming from American nearshoring efforts.
The outcome of the 2024 U.S. presidential election will undoubtedly further impact Mexico’s energy sector, especially as it relates to trade and investment. Sheinbaum’s industrial policy plans and interest in promoting a green economy align with Biden’s focus on the clean energy transition and nearshoring efforts. Conversely, a Trump White House may provide a more hostile and coercive environment for Sheinbaum to operate within.
Outlook
Given the current instability affecting the early stage of Claudia Sheinbaum’s administration, companies and investors need to adapt their current strategy to seize the right set of circumstances for their business.
Despite the undefined agenda for energy public policies and the ongoing debate between energy transition and oil investment, Sheinbaum will need to prioritise a stable domestic energy supply. Therefore, companies that want to be aligned with the government's agenda should invest in projects focused on new technologies that bolster domestic production or increase resilience.
Foreign companies may have concerns about the continuation of policies aligned with López Obrador’s approach, especially given the limited or even absent participation of private investment in Mexican oil companies in recent years. To mitigate this risk, companies can engage and promote public-private partnerships, which can foster joint ventures. However, joint ventures can present risk in the case of the nationalisation of foreign companies, but this is unlikely to occur under Sheinbaum’s presidency. Investors should focus on sectors that are likely to receive government support, such as technologies that enhance energy independence or generate a constant supply.
It is important to mention that there will be clearer indications if Sheinbaum will prioritise climate commitments or follow the steps of her predecessor in due course. Additionally, the outcome of the US elections is likely to significantly impact the country’s energy policy framework.
The U.S. LNG Pause: Implications for the Global Fertiliser and Food Markets
Peter Fawley
The U.S. LNG Pause
On January 26, the Biden administration announced a temporary pause on approvals of new liquified natural gas (LNG) export projects. The pause applies to proposed or future projects that have not yet received authorisation from the United States (U.S.) Department of Energy (DOE) to export LNG to countries that do not have a free trade agreement (FTA) with the United States. This is significant as many of the largest importers of U.S. LNG–including members of the European Union, the United Kingdom, Japan, and China–do not have FTAs with the United States. Without the DOE authorisation, an LNG project will not be allowed to export to these countries. The policy will not affect existing export projects or those currently under construction. The Department of Energy has not offered any indication for how long the pause will be in effect.
This pause will have political and economic implications across the globe, and is expected to apply further pressure to the LNG market, fertiliser prices, and agricultural production. The following analysis will first delve into the rationale for the pause, the expected impact it will have on global LNG supplies, and the associated risks this poses for the fertiliser and food markets. It will then examine the impact of this policy change on India’s agricultural sector, given that the country is heavily reliant on LNG imports to manufacture fertilisers for agricultural production. The article will conclude with brief remarks about the pause.
Reasons for the Pause
According to the Biden administration, the current review framework is outdated and does not properly account for the contemporary LNG market. The White House’s announcement cited issues related to the consideration of energy costs and environmental impacts. The pause will allow DOE to update the underlying analysis and review process for LNG export authorisations to ensure that they more adequately account for current considerations and are aligned with the public interest.
There are also likely political motivations at play, given the upcoming election in the United States. Both climate considerations and domestic energy prices are expected to garner significant attention during the lead up to the 2024 U.S. presidential election. The Biden administration has been under increasing pressure from environmental activists, the political left, and domestic industry regarding the U.S. LNG industry’s impact on climate goals and domestic energy prices. In fact, over 60 U.S policymakers recently sent a letter to DOE urging its leadership to reexamine how it factors in public interests when authorising new licences for LNG export projects.
These groups have argued that the stark increase in recent U.S. LNG exports is incompatible with U.S. climate commitments and policy objectives, as the LNG value chain has a sizeable emissions footprint. Moreover, there is a concern about the standard it sets for future policy. An implicit and uncontested acceptance of LNG could signal that the U.S is wholly committed to continued use of fossil fuels as an energy source, leading to more industry investments in fossil fuels at the expense of renewable energy technologies. In an unusual political alliance, large U.S. industrial manufacturers are lobbying alongside environmentalists to curb LNG exports. These consumers, who are dependent on natural gas for their manufacturing processes, worry that additional LNG export projects will raise domestic natural gas prices. Therefore, the pause may then be interpreted as an acknowledgement of these concerns and an attempt to reassure supporters that the Biden administration is committed to furthering its climate goals and securing lower domestic energy prices.
Impact on LNG Supplies
Since the pause only pertains to prospective projects, there will be no impact on current U.S. LNG export capacity. However, the pause may constrain supply and reduce forecasted global output as the new policy indefinitely halts progress on proposed LNG projects that are currently awaiting DOE authorisation. In the long-term, this announcement has the potential to tighten the LNG market, potentially resulting in increased natural gas prices and other commercial ramifications. Because the U.S. is currently the world’s largest LNG exporter, a drop in expected future U.S. supplies may force LNG importers to seek to diversify their supply. Some LNG buyers will likely redirect their attention to other, more certain sources of LNG, such as Qatar or Australia. Additionally, industry may be more keen to invest in projects in countries that have less regulatory ambiguity related to LNG projects.
Risk for the Global Fertiliser and Food Markets
Natural gas is key to the production of nitrogen-based fertilisers, which are the most common fertilisers on the market. With regard to the use of natural gas in fertiliser production, most of it (approximately 80 per cent) is employed as a raw material feedstock, while the remaining amount is used to power the synthesis process. Farmers and industry prefer natural gas as a feedstock as it enables the efficient production of effective fertilisers at the least cost.
The U.S. pause on new LNG projects is an unsettling signal to already fragile natural gas markets given the existence of relatively tight current supplies and a forecasted shortfall in future supply levels. This announcement will exacerbate vulnerabilities and put increased pressure on global supplies, potentially leading to greater volatility and price escalation. Additionally, increased global demand for natural gas will further strain the LNG market. Therefore, global fertiliser prices may increase given that natural gas is an integral input in fertiliser production. Natural gas supply uncertainty stemming from the U.S. announcement may not only impact market prices for fertiliser, but could also increase government subsidies needed to support the agricultural industry to protect farmers from price volatility. Due to the increased subsidy outlay, government expenditure on other publicly-funded programs could plausibly be reduced.
The last time there was a significant shock to the natural gas market, fertiliser shortages and greater food insecurity ensued. Following the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine, there was a stark increase in natural gas prices, which led to a rise in the cost of fertiliser production. This prompted many firms to curtail output, causing fertiliser prices to soar to multi-year highs. Higher fertiliser costs will theoretically induce farmers to switch from nitrogen-dependent crops (e.g., corn and wheat) to less fertiliser-intensive crops or decrease their overall usage of fertilisers, both of which may jeopardise overall agricultural yield. Given that fertiliser usage and agricultural output are positively correlated, surging fertiliser costs in 2022 translated into higher food prices across the world. While inflationary pressures have subsided in recent time, global food markets remain vulnerable to fertiliser prices and associated supply shocks. This is especially true for countries that are largely dependent on their agricultural industry for both economic output and domestic consumption. Food insecurity and global food supplies may also be further constrained by unrelated impacts on crop yields, such as extreme weather and droughts.
Case Study: India
The future LNG supply shortfall and its impact on fertiliser and food markets may be felt most acutely by India. The country is considered an agrarian economy, as many of its citizens – particularly the rural populations – depend on domestic agricultural production for income and food supplies. Fertiliser use is rampant in India and the country’s agricultural industry relies heavily on nitrogen-based fertilisers for agricultural production. With a steadily rising population and a finite amount of arable land, expanded fertiliser usage will be necessary to increase crop production per acre. As a majority of India’s fertiliser is synthesised from imported LNG, the expected increased demand for fertiliser will necessitate more LNG imports.
LNG imports to India are projected to significantly rise in 2024, with analysts forecasting a year-on-year growth of approximately 10 per cent. Over the long-term, the U.S. Energy Information Administration predicts that overall natural gas imports to India will grow from 3.6 billion cubic feet per day (Bcf/d) in 2022 to 13.7 Bcf/d in 2050, a 4.9 per cent average annual increase. The agricultural industry is a substantial contributor to this growth. This trend is only expected to continue, as India has announced that it plans to phase out urea (a nitrogenous fertiliser) imports by 2025 in order to further develop its domestic fertiliser industry. To ensure adequate supplies for domestic urea production, India is expected to increase its natural gas demand and associated reliance on LNG imports. A recent agreement between Deepak Fertilisers, a large Indian fertiliser firm, and multinational energy company Equinor exemplifies this. The agreement secures supplies of LNG (0.65 million tons annually) for 15 years, starting in 2026.
Concluding Remarks
The U.S. pause on new LNG export facilities will have ramifications for the global natural gas market and supply chain. While current export capacity will not be jeopardised, the policy change will delay future projects and may put investment plans into question. The pause will also have implications for downstream markets in which natural gas is an important input, such as the fertiliser market. There are a couple of questions that now loom over the LNG industry: (1) what will be the duration of the pause; and (2) to what extent will the pause affect LNG markets?
While the U.S. Department of Energy has given no firm timeline for the pause, analysts estimate – based on previous updates – that the DOE review will likely last through at least the end of 2024. The expectation is that the longer the pause remains in effect, the more uncertainty it will create, especially as it relates to private industry investment decisions and confidence in U.S. LNG in the long-term. In addition to the fertiliser and food markets, transportation, electricity generation, chemical, ceramic, textile, and metallurgical industries may all be affected by the pause. One potentially positive consequence is that because LNG is often thought of as a transitional fuel (between coal and renewable energies), a large enough impact on LNG supplies could accelerate the energy transition directly from coal to renewable sources of energy, providing a boost to the clean energy technologies market. However, the pause may also create tensions with trading partners as it could be interpreted as an export control or a discriminatory trade practice, both of which stand in violation of the principles of the multilateral rules-based trading system. This may expose the U.S. to potential challenges and disputes at the World Trade Organization. Although it may be some time before we are provided concrete answers to these questions, the results of the 2024 U.S. presidential election will provide some insight into what LNG policies in the U.S. will look like going forward.
African Green Hydrogen Exports: What are the risks?
Following Europe’s recent scramble for Africa’s natural gas resources due to the Russian invasion of Ukraine, Europe is now increasingly investing in the development of green hydrogen projects on the continent. Given Africa’s significant renewable energy potential, driven by its substantial solar photovoltaic power potential, the continent is well equipped to develop large-scale green hydrogen projects to supply European demand. Whilst there may be significant economic pay-offs for African countries exporting hydrogen to Europe, with an estimated €1 trillion green hydrogen potential, there are also many risks in the development of the nascent industry which may inhibit long-term growth.
Source: International Renewable Energy Agency
European hydrogen plans
Hydrogen has become a key part of Europe’s decarbonisation plans in its net-zero goals. Despite currently accounting for less than 2% of Europe’s energy consumption, the EU is aiming to ramp up production over the next decade. With the introduction of the REPowerEU plan in May 2022, the European Commission (EC) clearly stated its intention to utilise renewable hydrogen as an important energy carrier in its attempt to reduce its reliance upon Russia's fossil fuel imports. The EU plans to produce 10 million tonnes and import 10 million tonnes of renewable hydrogen by 2030.
The EU has planned to secure strategic partnerships with developing African nations such as Namibia and Egypt to ensure that they have a secure supply of renewable hydrogen. The incentives built into the EU regulations, enticing African nations to develop green hydrogen export facilities to Europe, could come at the expense of local populations. The energy poverty of many African nations, particularly in sub-Saharan Africa, has led many to argue that their domestic energy needs should be prioritised over helping the EU deliver its climate strategy.
The EU and individual European nations have already begun making huge commitments to green hydrogen in Africa, including provisions for exports from the continent to serve Europe’s domestic needs. The recent signing of a $34 billion agreement for a giant green hydrogen project in Mauritania is just one of those developments. Similarly, some European nations are working on hydrogen pipeline projects in Africa to meet their climate targets and to provide more secure energy supplies in future. Such projects include the “SoutH2 Corridor” pipeline project connecting North Africa with Italy, Austria, and Germany. The energy ministries in the respective countries have all signed a joint letter of political support for developing the 3,300-kilometre-long hydrogen pipeline corridor.
Source: Offshore Energy
Risk to African nations
Economic feasibility
Whilst many European nations emphasise Africa’s huge renewable energy to create green hydrogen, there are also significant economic risks that remain in its development. According to a study by the European Investment Bank, International Solar Alliance and the African Union, large-scale green hydrogen generation can enable African nations to supply 25 million tons of green hydrogen to global energy markets, equal to 15% of the current amount of gas used in the EU. The study also reported that green hydrogen is economically viable at €2/kg, due to the abundant availability of solar energy, enabling the possibility of low-carbon economic growth across the continent and reducing emissions by 40%. With more than 52 green hydrogen projects in Africa having been already announced, and production set to reach 7.2 million tonnes by the end of 2035, African nations look set to have massive increases in GDP, whilst also benefitting from the many new permanent and skilled jobs generated across the continent.
However, policymakers must be cautious to fully weigh up the economic feasibility of such projects. Limited transportation infrastructure makes transporting hydrogen which costly and hardly economically competitive. Even maritime shipping, the most cost-effective method for distances over 3,000km, would cost an estimated additional$1 to $2.75/kg. For shorter distances, the cost of pipeline transport could be significantly lower, estimated at$0.18/kg per 1,000km for new hydrogen pipelines and $0.08/kg for retrofitted gas pipelines. Given its economic competitiveness, hydrogen pipelines are the preferred choice of transportation for European nations, with the EU set to provide huge subsidies for a proposed hydrogen pipeline, named the“South Corridor”, stretching from North Africa to Bavaria. Nevertheless, as the green hydrogen industry is at a very early stage of development, it is very difficult to predict how the market will grow in the long term and accurately predict the economic payoffs of hydrogen pipelines for African nations. The demand for hydrogen could vary from150 to 500 million metric tonnes/year by 2050 due to the level of worldwide climate goals, specific actions taken within various sectors, efforts to enhance energy efficiency, direct electrification, and the adoption of carbon capture technologies. Therefore, if the European market does not develop at the speed and scale expected, African nations investing in green hydrogen will be left with huge debts to be paid for by their populations.
Source: IEA
2. Energy poverty
The potential development of green hydrogen exports to Europe should also not overshadow Africa’s broader energy landscape. At present, 600 million people, primarily located in sub-Saharan Africa and equivalent to 43% of the total African population, lack access to electricity. Sub-Saharan Africa (excluding South Africa) consumes approximately 180 kWh of energy per capita, compared to 13,000 kWh per capita in the U.S. and 6,500 kWh in Europe. Renewables also remain in their infancy in Africa, with approximately 180 TWh of renewable power generated in Africa in 2018, equivalent to approximately less than 0.02% of its estimated potential. African nations must be cautious to ensure that they choose the correct trade-off between utilising hydrogen for exports to Europe and their own domestic needs. Should African nations divert their resources toward hydrogen production for exports, some fear that green hydrogen may become another “neo-colonial resource grab” and starve African nations of their resources.
Therefore, African nations must ensure that all the benefits of green hydrogen exports are not extracted for European gain. The agreements between the EU and African nations such as Egypt, Morocco and Namibia already show worrying signs of resource exploitation. Despite these deals being presented as a win-win scenario, the rules allow hydrogen projects to “cannibalise” the local infrastructure for exports. Namibia is a prime example as it is racing to become Africa’s first green hydrogen exporting hub despite only 56% of its citizens having access to electricity in 2022 and relying upon imports to meet its electricity demand. The Namibian government hopes to develop 10 hydrogen export projects with European nations. However, there are concerns over potential misuse of climate finance, which should focus on aiding local development, rather than export projects.
Outlook
With increasing interest and investment from European nations into green hydrogen projects in Africa, countries on the continent must remain cautious of the huge benefits promised by their European counterparts. Despite the continent's unparalleled potential for producing low-cost green hydrogen in the future, producing green hydrogen at economically competitive prices remains elusive given the high costs of production and transportation. However, should these costs be brought down by increased European investment, African nations may well prioritise meeting their own domestic energy demands and accelerating domestic renewable energy deployment before considering exporting green hydrogen to Europe in large-scale quantities.
Powering the future: Cobalt in the EV battery value chain
Powering the future: Cobalt in the EV battery value chain
This research paper sheds light on the key risks associated with the supply of cobalt, a critical mineral for the production of electric vehicle (EV) batteries. With demand for EVs projected to grow steadily in the coming decade, it is crucial that companies mitigate these risks. The concentration of finite cobalt reserves in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) and the concentration of refining capacities in China create a delicate balance of supply that is highly risk prone.
India’s Lithium Rush: Supply Chains, Clean Energy, and Countering China
The discovery of vast lithium deposits in the Indian territory of Jammu and Kashmir is being hailed as a win for the country’s clean energy transition. With the government already promoting domestic EV manufacturing, this could prove to be one of the missing pieces for the puzzle of an Indian EV supply chain.
Background
With rising demand for portable electronics and a push for a low-carbon future, lithium has become one of the most important minerals. Given its application in lithium-ion batteries, it is vital for powering everything from electric vehicles and portable electronics to stationary energy storage systems.
In particular, Lithium-ion battery demand from EVs is set to rise sharply, from the current 269 gigawatt-hours in 2021 to 2.6 terawatt-hours (TWh) per year by 2030 and 4.5 TWh by 2035. According to BloombergNEF’s (BNEF) Economic Transition Scenario (ETS) – which assumes no additional policy measures – global sales of zero-emission cars will rise from 4% of the global market in 2020 to 70% by 2040. Consequently, the global supply chain for lithium has become increasingly important.
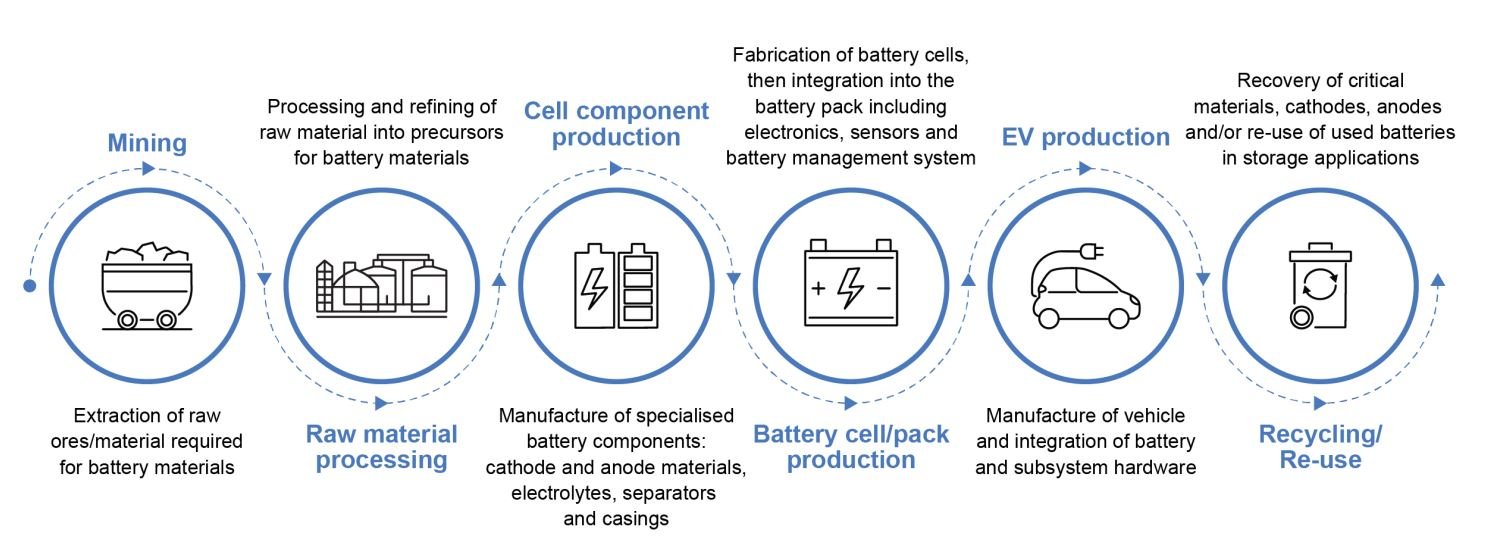
EV battery supply chain. Image credit: International Energy Agency
The lithium supply chain is complex, involving multiple stages and players, and is subject to geopolitical and economic factors. Most of the world’s lithium deposits are in the ‘Lithium Triangle’ of the world in South America – Chile, Argentina, and Bolivia. Of these three, however, only Chile Ranks amongst the list of the world’s top lithium producers, headed by Australia. Apart from production, China dominates both the refining and battery manufacturing in the EV battery value chain.
Source: Statista
India: The New Potential Partner of the World
Given the global geopolitical environment, singular dependence on China for a vital resource such as lithium has far-reaching strategic implications. Naturally, democratic nations across the world are prioritizing the reconfiguration of their supply chains for critical manufacturing inputs. Combining its demographic dividend, educated and sufficient workforce, and entrepreneurial spirit– India is rising as a potential and reliable partner. The European Union’s ‘China + 1’ strategy, the EU-India Trade and Technology council, the United States’ recent Initiative for Critical and Emerging Technologies (iCET), and Australia’s Economic Cooperation Trade Agreement with India – testify to the merit that the liberal-democratic world order sees in a partnership with India.
In the given friend-shoring environment that India enjoys, the recent discovery of 5.9 million tons of lithium in the country is monumental. India’s automobile sector itself is transforming. According to NITI Aayog, by 2030, 80% of two and three-wheelers, 40% of buses, and 30 to 70% of cars in India will be EVs. The newly found lithium can help the nation meet rising demand, both domestically and globally. India’s government has already been pushing for electric mobility and domestic EV manufacturing. The 2023-24 Union Budget, allocated INR 35,000 crore for crucial capital investments aimed at achieving energy transition, including efforts for electrification of at least 30% of the country's vehicle fleet by 2030 and net-zero targets by 2070. For EV manufacturers, the government has launched initiatives such as the Faster Adoption of Manufacturing of Electric Vehicles Scheme – II (FAME – II), allocating approximately $631 million towards subsidizing and promoting the adoption of clean energy vehicles.
Indian Lithium deposits: Risks and Challenges
The recent discovery in the Reasi district of the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir solves one of the major challenges to a localized li-ion battery supply chain in the country– access to lithium deposits. However, there are more challenges ahead.
Firstly, the Reasi district is just 100 kilometres from the Rajouri district, a geopolitically sensitive area. Although today these areas are well-connected to India with proper infrastructure, including airports and highways, the Line of Control between India and Pakistan is less than 100 kilometres from Rajouri and around 200 kilometres from Reasi. The region’s proximity to Azad Jammu and Kashmir also makes it vulnerable to militant activities. Greater infrastructural development in the region, including a robust logistics network will have to be developed to ensure an uninterrupted indigenous supply chain (given that other stages of the supply chain are also established domestically).
Secondly, although the Geological Survey of India (GSI) has the capacity to discover and locate lithium deposits, the remainder of the value chain to produce commercial-grade lithium indigenously is not in place. Similar to Australia, Canada, and China, the identified lithium reserves in India are in hard rock formations. In order to extract the resource, mining capabilities will first have to be established in the region. It is still unclear whether these reserves will be managed by state authorities or undertaken by the central government, given the strategic importance of the resource. Furthermore, whether the mines be auctioned, like India’scoal mines, or entrusted to a public sector enterprise, is not yet known.
Timely and major investment in developing refining, processing, and purification technologies will be required. India will have to build a large-scale capacity for transforming extracted material into high-purity lithium in order to take full advantage of this discovery. While the opportunity is considerable, so are the costs. India’s government will need to devise a clear strategy that effectively helps both the country’s energy transition and domestic manufacturing ambitions.
Image credit: Nitin Kirloskar via Flickr
Copper Shortages and the Transition to Green Energy
Copper, as a chemical element, is one of the most important because it is especially good at conducting heat and electricity, relative to other metals. It has multiple functions, including its use in industrial machinery and electronic equipment or as a raw material in the development and evolution of clean energies.
Copper, as a chemical element, is one of the most important because it is especially good at conducting heat and electricity, relative to other metals. It has multiple functions, including its use in industrial machinery and electronic equipment or as a raw material in the development and evolution of clean energies. Copper deficit for 2023 has already been announced, and it also symbolizes a period of crisis for plenty of projects and industries. The cause is an evident increase in demand and a severe supply constraint.
Supply-side factors
Most of the world’s suppliers are concentrated in Latin America, where the 10 most important mines are located: Chile (3), Peru (3) and Mexico (1). Unfortunately, a series of recent events have led to a shortage in the supply of copper. In fact, problematical political situations in some of these countries have exacerbated the current deficit. Some of them are:
PERU: It represents 10% of the world's copper supply.
As a consequence of the dismissal of Pedro Castillo for declaring the dissolution of the congress and the state of emergency, some unrest occurred in the last few months, affecting about 30% of copper production.
These are the main mines located in Peru:
- Antamina: It is the largest copper deposit in Peru and represents almost 20% of national production. In 2021, an indefinite suspension of operations was declared due to unrest caused by peasant communities blocking access to the facilities.
- Glencore's Antapaccay: This copper mine has been attacked several times in the first month of 2023 and protesters are demanding the cessation of the mine's operations. As a result, the mine temporarily halted its operations.
- MMG's Las Bambas: The mining company has halted and slowed down copper production due to transportation blockages, as in previous occasions what has been generated is an accumulation of production without being able to dispose of it.
CHILE: The major supplier. It represents 27% of the world copper supply.
Increasing environmental regulation has raised production costs in the mining industry and raised barriers to expansion, as happened with the Dominga mining megaproject due to its environmental impact.
Indeed, companies such as BHP Group, Antofagasta PLC y Freeport-McMoRan Inc. have postponed major investments in this business.
MEXICO: The same stance was adopted. Strict environmental mining regulations have stalled up to 25 major projects by freezing new mining concessions and taking a tougher line on the processing of environmental permits.
Therefore, the main causes of the supply constraints are regulatory concerns about their environmental impact and logistic problems related to the capacity to transport supplies (road blockades and protests) and the chaos generated by the protests, which has forced the suspension or interruption of mining companies’ activities.
In addition, during the first week of February, the operations of First Quantum Minerals, which operated in Panama and is considered one of the largest mines in Latin America, were suspended. The inconveniences this time were caused by disagreements with the Panamanian government in the payment of royalties and taxes.
Demand-side factors
The lack of balance between supply and demand is also due to the simultaneous increase in copper consumption in China, driven by a growth in its economic expansion, and its reopening of the market after the pandemic period. China is the world's largest copper consumer and has increased its demand due to the large investments and infrastructure projects that are on the way.
Along the same lines is the global project to move towards a green energy transition. In accordance with the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development (SGD), adopted by the member states of the United Nations and the goals set for 2050, a series of projects have been launched to achieve an efficient energy transition. In light of this planned transiation, copper has become an essential resource as it is essential for the replacement of fossil fuel-based power systems with renewable energy sources.
Therefore, the energy transition has led to a huge demand for copper. Indeed, annual demand will double to 50 million tons by 2035, raising the concern that shortages could result in a reversal of the course of the energy transition. This been seen already in industries such as as construction, manufacturing, architecture. Additionally, the automotive sector’s ability to produce electric vehicles on a large scale will be especially hindered by such shortages.
Summary
The halt in production in the world's main copper-producing regions has exacerbated the impact of increasing demand for copper. Cash-settlement prices for copper listed on the London Metal Exchange (LME) show a rapid increase in copper prices from $5,965 to $8,387 in the period between end of year 2018 to end of year 2022.So far this quarter the LME’s copper cash-settlements peaked at $9.436 on January 18. Experts predict that the price will remain above US$8,500 per tonne for the next few years, with the risk of even exceeding US$10,000.
Unfortunately, a similar situation may occur with other relevant minerals such as lithium and cobalt. In fact, copper experience will be a clear reference for other raw materials in order to find an effective solution.
In the end, it is all about balancing the dilemma between the environmental, social and governance (ESG) practices that are the main challenges of mining and increasing copper production to supply key sectors of the green transition and the economy.
All in all, the supply of copper will be substantially impaired by the following factors:
Copper is a necessary element in many manufacturing and construction industries, added to the growing demand in renewable energy projects that use this element as part of the transition.
The demand for copper from high consuming countries such as China will cause the supply and demand balance to become more unbalanced if a controlled supply solution is not found.
The lack of consensus between the private sector, the public sector and communities around mining will maintain the constant blockades and protests in the main copper-supplying cities in Latin America.
Environmental regulation is increasingly relevant for the development of the mining activity but has become a barrier to its operation.
The cessation of activities of the main mining companies abruptly generates a deficit in the copper supply, which has a direct impact on the price of copper, given the scarcity situation, expanding the damage caused by the initial problem.
Powering the future: Lithium in the EV battery value chain
Powering the future: Lithium in
the EV battery value chain
This research paper is the first in a series covering the numerous risks associated with electric vehicle (EV) battery production. Each paper delves into a specific mineral that is vital to this process, starting off with lithium. This series is brought by a team of analysts from the Global Commodities Watch.
REPowerEU, Piano Mattei, and the Political Economy of the Mediterranean
From the Phoenicians to the First French Republic, two shores of the Mediterranean have been the cradle for many important ancient civilizations, including the Carthaginians and Ancient Egyptians. Although in modern times the post-war political alignments and government institutions look very different, the evidence of a rich common history can be seen all over Southern Europe and North Africa in the forms of enclaves, architecture, and shared cultural and linguistic norms. Following Giorgia Meloni’s state visits to Algeria and Libya, this spotlight considers how Italy’s Piano Mattei (Mattei plan) can be an opportunity for the rest of the European Union (EU) to successfully implement the REPowerEU energy plan and potentially rekindle trans-Mediterranean trade and cooperation, beyond natural gas and energy markets.
Immigration, Energy Markets, and Fratelli d’Italia: What is Piano Mattei?
In simple terms, Piano Mattei represents Italy’s de facto foreign policy in the Mediterranean under Giorgia Meloni’s tenure as President of the Chamber of Deputies (the official title of the head of the Italian government). The origins of Mattei can be found in Fratelli d’Italia’s (FdI) manifesto for the 2022 Italian general election, which stresses FdI’s belief that Italy must once again become a leader in energy markets. Piano Mattei takes its name from Enrico Mattei – founder of Italy’s state-owned hydrocarbons agency: Ente nazionale idrocarburi (Eni). During his time in the Chamber of Deputies, and later as Chairman of Eni, Mattei realised that if Italy wanted to include natural gas in its energy mix then Italy needed to cooperate with key exporters. Indeed, Mattei oversaw the signing of various bilateral agreements with many newly-independent states in the MENA region to import natural gas to Italy. Mattei’s work with Eni was also crucial to the construction of the Transmed pipeline, which channels Algerian natural gas to Sicily via Tunisia. The plans for the Transmed pipeline also included the Maghreb-Europe pipeline, which exported Algerian gas to the Iberian Peninsula until last October, when Algiers elected to not renew its export contracts with Morocco over increasing tensions over the Western Sahara conflict. This effectively ceased the flow of natural gas from Algeria to Iberia.
Giorgia Meloni formally introduced Piano Mattei last December, during the eighth iteration of the Dialoghi Mediterranei di Roma – a forum on Mediterranean politics hosted by Italy’s Ministry of Foreign Affairs and International Cooperation alongside the Instituto per gli studi di politica internazionale (ISPI), a prominent Italian thinktank. In Meloni’s own words, Piano Mattei is a “virtuous collaboration leading to the growth of the European Union and African nations” guided by the principles of “interdependence, resilience, and cooperation”. Naturally, the namesake “Mattei” suggests that Meloni’s stance is primarily to secure energy supplies for Italy and totally eliminate the dependence on Russian natural gas. On the one hand, however, Meloni’s foreign policy in the Mediterranean also aims to build upon the European Commission’s trade ambitions with the ‘Southern Neighbourhood’: “The long-term objective of the trade partnership between the EU and its Southern Neighbourhood is to promote economic integration in the Euro-Mediterranean area, removing barriers to trade and investment” and the EU’s wider energy policy goals. On the other hand, Associazione Amici dei Bambini – an Italian children’s rights NGO – raises the concern that Meloni’s ambiguous and rhetorical references to immigration in her keynote speech at the Dialoghi Mediterranei di Roma, suggest that perhaps Meloni’s ambitions are centred on delivering campaign promises regarding trans-Mediterranean migration flows. Indeed, Meloni’s lexical and rhetorical ambiguity is often the cause for concern for some analysts (including the author of this spotlight). Whether Meloni intends to use Mattei to further her immigration policies is difficult to ascertain at this stage, and is beyond the scope of this spotlight.
Regardless of how one may interpret the scope or intentions of Mattei, one thing is certain – it can be an opportunity for all of the Mediterranean countries. For Italy (and to a large extent, Meloni) it would be a first step in re-establishing itself as a regional economic powerhouse and help move away from decades’ long economic stagnation. For Algeria and other North African countries, the prospect of increased cooperation and interdependence with the EU is an incentive for investment, potentially beyond natural gas and energy markets. In the two weeks after Meloni’s visit to Algiers on January 24 2023, Eni’s (Euronext Milan) share price increased 4.58 per-cent from €14.18 to €14.83. Year-to-date growth is around the 8 per-cent mark, at time of writing.
Limits for the European Commission and Meloni’s Government
Although a more collaborative and economically interdependent Mediterranean could have the potential to benefit states on either side, Giorgia Meloni and the European Commission need to learn from the past if they are to derive short-term economic benefit as well as long-term regional cohesion. What is meant here by “learning from the past” is that ‘switching’ who is supplying the EU with gas from Russia to Algeria, for example, does not account for the weakness in Europe’s energy strategy before the Russo-Ukrainian War. That is, relying on a weakly-integrated trade partner for a crucial commodity.
The REPowerEU plan outlines the EU’s energy policy following the Russian invasion of Ukraine. Although the medium to long-term impetus is to increase the role of renewables within the bloc’s energy mix, the short-term imperative includes securing hydrocarbons from non-Russian suppliers. These two foreign policy goals are not necessarily ad diem, and in the context of the Mediterranean, actually involve compromising successful economic interdependence between the EU and its ‘Southern Neighbourhood’.
To contextualise; on January 19 2023 Resolution 2023/2506 was adopted by the European Parliament, calling upon the Kingdom of Morocco to “release all political prisoners'', including the release of Nasser Zefzafi, and to “end of the surveillance of journalists, including via NSO’s Pegasus spyware, and to implement legislation” which protects journalists. Further, increasing collaboration with Algeria (who, as above mentioned, is having its own political standoff with Morocco over Western Sahara) suggests that the short and medium-term ambitions of REPowerEU and Piano Mattei are at odds with the European Parliament’s adoption of Resolution 2023/2506. This is problematic for securing natural gas supplies to Iberia and the westernmost corners of the bloc, but potentially for regional stability in general. If the EU cannot strike the right balance between appeasing Algerian requests and reprimanding Morocco for its treatment of journalists, the prospect of tensions between the two North African states cooling off is not particularly positive. This indirectly impacts the operations of the Maghreb-Europe pipeline, and so on. Indeed, on January 23 2023 the Moroccan parliament “voted unanimously” to reconsider its ties with the European Parliament.
That said, Morocco-European relations are not exactly at an all time low – in terms of trade and commerce, at least. Trade between the EU and Morocco has increased significantly in the period between 2011 and 2021, and the North African state is the bloc’s 19th largest trading partner. Morocco is also among the top African trading partners for Greece, Italy, Portugal, and Spain. Therefore, there is still space for Morocco-Europe relations to improve within the broader scope of REPowerEU, the European Commission’s ‘Southern Neighbourhood’, and of course, Giorgia Meloni’s Piano Mattei.
Summary: Implications for the Political Economy of the Mediterranean
As the EU gravitates towards North Africa to ‘de-Russify’ its natural gas imports what diplomats and politicians should keep in mind two things: (i) the current tension between Algeria and Morocco, and (ii) diversifying gas imports is not (in the short-term) compatible with holding Morocco politically accountable for its mistreatment of journalists. It is an unlaudable conclusion, of course. But certain international relations theory – namely liberal institutionalism – would defend this claim as the theory emphasises understanding “the role that common goals play in the international system and the ability of international organisations to get states to cooperate,” as opposed to focussing strictly on power relations between states.
In the case of Mattei as a part of the EU’s ‘Southern Neighbourhood’ strategy, turning to the Mediterranean region means understanding the political tensions of North Africa in order to ensure the best outcomes for REPowerEU and Mattei, as well as avoiding antagonising the Kingdom of Morocco – even if the normative reasons for doing so are justified. Within the EU, the success of Piano Mattei in increasing Algerian gas supplies to Italy and the rest of the Transmed pipeline (which terminates in Slovenia) is intricately linked with REPowerEU’s short-term goals. Thus, as Arturo Varvelli elaborates in his commentary on the issue, Brussels and Rome ought to conduct themselves in a cooperative manner to ensure the success of Mattei and REPowerEU alike. If not, Meloni’s well-documented Euroscepticism could well be weaponised and used against Brussels, which would be a counterproductive outcome for Italy and the EU’s political legitimacy.
On these premises, then, the EU’s ‘Southern Neighbourhood’ strategy should also encompass the goals of REPowerEU to, first of all, secure alternative gas supplies, but also to cosy up to Rome and using the increased demand for non-Russian natural gas to quell Algiers-Rabat tensions. Equally, in pursuing the energy goals of Piano Mattei Giorgia Meloni should also consider using Italy’s diplomatic power to help find a solution that might reopen the Maghreb-Europe pipeline if she desires to obtain a reputation for closing deals and power brokering at the European level.
Outlook
Italian-North African gas exploration and trade deals may face significant challenges in the shape of Europe’s green energy transition.
Meloni will most likely be able to secure the ‘de-Russification’ of Italy’s natural gas supply, but whether this will hamper Rome’s green energy transition remains to be seen.
Forecasts would suggest that LNG futures prices will not fluctuate sufficiently to dampen the value of natural gas trade between Italy and its partners, Algeria and Libya, in North Africa.
Whether Meloni aims to cooperate with, or conspire against, the EU’s short and long-term energy policies remains to be seen.
At the present moment it is very unlikely that Algeria-Morocco relations will improve to the point of reopening gas flows to Iberia via the Maghreb-Europe pipeline. How the situation between both states remains a critical point for the energy policies of Italy and the EU at large.
Image Credits: ROSI Office Systems Inc.
Africa in the “white gold” rush
The global supply of lithium ore has become an increasingly tangible bottleneck as many countries move towards a green transition. The International Energy Agency (IEA) predicted that the world could face a shortage of this key resource as early as 2025, as demand continues to grow. The increasing popularity of electric vehicles (EVs), which saw sales double in 2021, as well as other products which require lithium batteries, have been primary factors in this supply crunch.
Demand for lithium (lithium carbonate in this case) has driven high prices, which also nearly doubled in 2022, over $70,000 a tonne, and put pressure on the mining industry to increase production. This has led to heightened competition over this strategic resource and a rush to explore new reserves. An emerging arena in this competition has been Sub-Saharan Africa which has the potential to become a major player in lithium production, behind already established producers in South America and Australia. This region does, however, pose a unique set of challenges for lithium production in terms of infrastructure as well as a diverse and risk prone political constellation.
Within the region there are several countries which have already been tapped as potential producers or have already developed some degree of extraction capacity. Among these are Mali, Ghana, the DRC, Zimbabwe, Namibia and South Africa, at this stage most of these countries are at some stage of exploration, development or pre-production, currently only Zimbabwean mines are fully operational.
The political instability in some of these countries is a primary concern in the future of lithium production. Mali stands out in this regard with the withdrawal of the French intervention force in 2022, after nearly 10 years, and the ensuing power vacuum. In other countries such as the DRC political risk has been largely tied to corruption in governance which limits competition potential as well as human rights and environmental concerns which emerged around cobalt mining.
Zimbabwe offers a perspective into the most developed lithium operation in the region. In early 2022, Zimbabwe’s fully operational Bitka mine was acquired by the Chinese Sinomine Resource Group. Also in 2022, Premier African Minerals, the owners of the pre-production stage Zulu mine, concluded a $35 million deal with Suzhou TA&A Ultra Clean Technology Co. which was set to see first shipments in early 2023. This was followed by a similar $422 million acquisition of Zimbabwe's second pre-production mine Arcadia by China’s Zhejiang Huayou Cobalt.
Zimbabwe’s government responded to this mining boom by banning raw lithium exports stating that “No lithium bearing ores, or unbeneficiated lithium whatsoever, shall be exported from Zimbabwe to another country.” This move is intended to keep raw ore processing within the country, and despite initial appearances will not apply to the Chinese operation, whose facilities already produce lithium concentrates. Yet, this policy does demonstrate the active role that the government is able to play in the market, and their willingness to harness this economic windfall.
Even the most developed lithium mining operations in the region must pay close attention to the political situation unfolding around them. As competition over this strategic resource becomes more acute, the role of soft power will likely play a key role in negotiating favourable terms and preferential treatment in the exploitation of lithium reserves.